The Importance of IT Support for Small Businesses

In today’s digital age, small businesses face a multitude of challenges, from managing daily operations to maintaining customer relationships. One critical aspect that often gets overlooked is the importance of robust IT support. In a landscape where technology drives efficiency and competitiveness, having reliable IT support can be the difference between thriving and merely surviving.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
IT support plays a pivotal role in streamlining operations. Small businesses often operate with limited resources, making it crucial to maximize efficiency. A well-structured IT support system helps in automating routine tasks, managing data effectively, and ensuring that systems run smoothly. This means fewer disruptions, reduced downtime, and the ability for employees to focus on their core responsibilities rather than troubleshooting technical issues.
2. Cybersecurity Protection
Cyber threats are a significant concern for businesses of all sizes, but small businesses are particularly vulnerable. Many small enterprises believe they are too small to be targeted, yet statistics show otherwise. Cybercriminals often target smaller businesses due to their perceived lack of robust security measures. IT support is essential for implementing strong cybersecurity protocols, including firewalls, antivirus software, and employee training on best practices. With effective IT support, small businesses can protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and avoid costly breaches.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Hiring a full-time IT department can be financially burdensome for small businesses. IT support services offer a cost-effective solution by providing access to expert help on an as-needed basis. Whether through managed IT services or outsourcing specific tasks, small businesses can enjoy high-quality support without the overhead costs associated with a full-time staff. This flexibility allows businesses to scale their IT support according to their specific needs.
4. Access to Expertise
Small businesses may lack the in-house expertise required to tackle complex IT issues. IT support provides access to a pool of knowledgeable professionals who stay updated on the latest technology trends and solutions. This expertise can be invaluable in selecting the right tools and systems that align with the business’s goals. Moreover, these professionals can offer strategic advice on how to leverage technology for growth and efficiency.
5. Improved Customer Service
In an era where customer expectations are high, IT support can enhance customer service efforts. Effective IT systems facilitate better communication channels, CRM systems, and data analytics tools that help businesses understand and respond to customer needs. With IT support ensuring these systems run smoothly, businesses can provide timely and effective service, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Every business faces risks, from natural disasters to cyberattacks. IT support is crucial for developing and implementing disaster recovery plans that ensure business continuity. This involves regular data backups, system redundancies, and protocols for quickly restoring operations after a disruption. For small businesses, being prepared for the unexpected can mean the difference between recovery and total loss.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
As small businesses grow, their IT needs evolve. IT support provides the scalability and flexibility required to adapt to changing circumstances. Whether it’s integrating new software, upgrading hardware, or expanding to remote work solutions, having a responsive IT support system in place ensures that businesses can adapt without major disruptions. This scalability is particularly important for seasonal businesses or those experiencing rapid growth.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries have specific regulations regarding data management and cybersecurity. IT support helps small businesses navigate these complex compliance landscapes. By ensuring that systems and processes meet regulatory requirements, IT support minimizes the risk of penalties and legal issues. This proactive approach not only safeguards the business but also builds credibility with clients and partners.
9. Fostering Innovation
With the right IT support, small businesses can explore innovative technologies that enhance their offerings. Whether it’s adopting cloud computing, utilizing big data analytics, or exploring artificial intelligence, having expert guidance allows businesses to implement these technologies effectively. Innovation can lead to improved products and services, opening new revenue streams and creating a competitive edge.
10. Focus on Core Business Functions
Perhaps one of the most significant benefits of IT support is the freedom it provides small business owners. By outsourcing IT management, business owners can focus on what they do best—growing their business and serving their customers. This shift in focus not only increases productivity but also fosters a more strategic approach to business development.
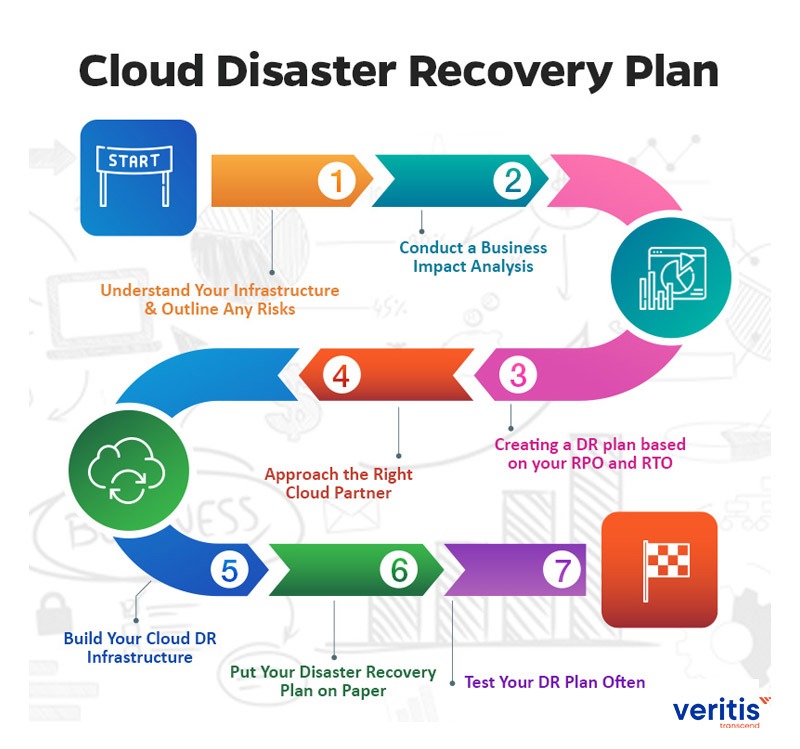
How to Create an Effective IT Disaster Recovery Plan
In today’s digital landscape, businesses rely heavily on technology for their daily operations. However, unforeseen disasters—ranging from cyberattacks and natural disasters to hardware failures—can disrupt these operations and threaten business continuity. An effective IT disaster recovery plan (DRP) is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring that a business can recover quickly and efficiently. This guide outlines the key steps to create an effective IT disaster recovery plan.
1. Understanding the Importance of a Disaster Recovery Plan
Before diving into the specifics of creating a DRP, it’s essential to understand why it is necessary. A disaster recovery plan:
- Protects Data: Safeguarding critical data ensures that vital business information is not lost during a disaster.
- Ensures Business Continuity: A well-structured plan helps maintain essential functions, minimizing disruptions.
- Builds Customer Trust: Having a DRP demonstrates to clients that the business is prepared for emergencies, fostering trust and loyalty.
- Complies with Regulations: Many industries have specific regulations that mandate data protection and disaster recovery protocols.
2. Conduct a Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
The first step in creating a DRP is to conduct a Business Impact Analysis. This process identifies critical business functions and the potential impact of a disaster on these functions. Key elements to consider include:
- Identify Critical Systems: Determine which IT systems and applications are essential for business operations.
- Assess Downtime Tolerance: Evaluate how much downtime each critical system can tolerate without causing significant harm.
- Analyze Dependencies: Identify dependencies between systems, applications, and personnel to understand how failures may impact one another.
3. Define Recovery Objectives
Once the BIA is complete, define key recovery objectives. This includes:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable amount of time that a system can be down after a disaster.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This indicates how frequently data should be backed up to minimize losses.
Setting clear RTO and RPO metrics helps guide the disaster recovery strategies and ensures alignment with business needs.
4. Develop a Disaster Recovery Strategy
With a clear understanding of critical systems and recovery objectives, the next step is to develop a disaster recovery strategy. This strategy may include:
- Data Backup Solutions: Establish regular backup processes, whether on-site, off-site, or using cloud-based solutions. Ensure that backups are tested regularly for reliability.
- Redundancy Measures: Implement redundant systems or failover solutions to minimize downtime in case of a system failure.
- Cloud Disaster Recovery: Consider cloud-based DR solutions that offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to recover data and applications quickly.
5. Create a Detailed Recovery Plan
The recovery plan should outline the specific steps to be taken in the event of a disaster. Essential components include:
- Emergency Contacts: A list of key personnel, including IT staff, management, and vendors, who need to be contacted during a disaster.
- Step-by-Step Procedures: Detailed instructions for restoring systems, data, and applications. This should include prioritization based on the criticality of each system.
- Communication Plan: Outline how information will be communicated to employees, stakeholders, and customers during and after a disaster.
6. Test the Disaster Recovery Plan
Creating a plan is only the first step; testing it is equally important. Regular testing ensures that the plan is effective and that all personnel understand their roles during a disaster. Testing methods can include:
- Tabletop Exercises: Conduct discussions and simulations to walk through the plan without actual recovery efforts.
- Full-Scale Drills: Simulate a disaster scenario to test the recovery procedures in real-time. This helps identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Review and Update: After each test, gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to the plan. This should be an ongoing process as business needs and technologies evolve.
7. Train Employees
Effective disaster recovery relies on well-informed employees. Conduct training sessions to ensure that all staff members understand the disaster recovery plan, their roles, and the importance of data protection. Regular training reinforces the plan and prepares employees for potential emergencies.
8. Review and Update the Plan Regularly
A disaster recovery plan is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous review and updates. Regularly assess the plan to account for:
- Changes in Technology: New systems, software, and hardware may alter the recovery process.
- Business Growth: As the business evolves, the critical systems and applications may change, necessitating updates to the DRP.
- Regulatory Requirements: Keep abreast of any changes in regulations that may impact data protection and recovery protocols.
Establish a regular schedule for reviewing and updating the disaster recovery plan, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
9. Invest in the Right Tools and Technologies
To support the disaster recovery plan, invest in tools and technologies that facilitate quick recovery. This may include:
- Backup Solutions: Reliable and secure backup solutions that automate data backups and offer quick restoration options.
- Monitoring Tools: Systems that monitor network performance and alert IT staff to potential issues before they escalate into disasters.
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Consider outsourcing disaster recovery to specialized service providers that offer comprehensive DR solutions.
10. Establish a Budget for Disaster Recovery
Finally, allocate a budget specifically for disaster recovery efforts. This budget should cover tools, training, regular testing, and any additional resources needed to ensure effective recovery. Investing in disaster recovery is a proactive approach that can save businesses from significant losses in the event of a disaster.
